‘Realistic’ new model points the way to more efficient and profitable fracing
LOS ALAMOS, N.M. -- A new computational model could potentially boost efficiencies and profits in natural gas production by better predicting previously hidden fracture mechanics. It also accurately accounts for the known amounts of gas released during the process.
“Our model is far more realistic than current models and software used in the industry,” said Zdeněk Bažant, McCormick Institute professor and Walter P. Murphy professor of civil and environmental engineering, mechanical engineering, and materials science and engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering. “This model could help the industry increase efficiency, decrease cost, and become more profitable.”
Despite the industry’s growth, much of the fracing process remains mysterious. Because fracing happens deep underground, researchers cannot observe the fracture mechanism of how the gas is released from the shale.
“This work offers improved predictive capability that enables better control of production while reducing the environmental footprint by using less fracturing fluid,” said Hari Viswanathan, computational geoscientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory. “It should make it possible to optimize various parameters such as pumping rates and cycles, changes of fracturing fluid properties such as viscosity, etc. This could lead to a greater percentage of gas extraction from the deep shale strata, which currently stands at about 5% and rarely exceeds 15%.”
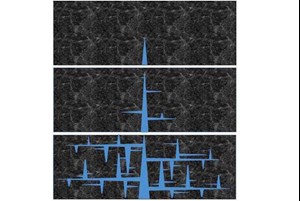
By considering the closure of preexisting fractures caused by tectonic events in the distant past and taking into account water seepage forces not previously considered, researchers from Northwestern Engineering and Los Alamos have developed a new mathematical and computational model that shows how branches form off vertical cracks during the fracing process, allowing more natural gas to be released. The model is the first to predict this branching while being consistent with the known amount of gas released from the shale during this process. The new model could potentially increase the industry’s efficiency.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Jan. 11, in a paper titled Branching of Hydraulic Cracks in Gas or Oil Shale with Closed Natural Fractures: How to Master Permeability.
Understanding just how the shale fractures form could also improve management of sequestration, where wastewater from the process is pumped back underground.
To extract natural gas through fracing, a hole is drilled down to the shale layer — often several kilometers beneath the surface — then the drill is extended horizontally, for miles. When water with additives is pumped down into the layer under high pressure, it creates cracks in the shale, releasing natural gas from its pores of nanometer dimensions.
Classic fracture mechanics research predicts that those cracks, which run vertically from the horizontal bore, should have no branches. But these cracks alone cannot account for the quantity of gas released during the process. In fact, the gas production rate is about 10,000 times higher than calculated from the permeability measured on extracted shale cores in the laboratory.
Other researchers previously hypothesized the hydraulic cracks connected with pre-existing cracks in the shale, making it more permeable.
But Bažant and his fellow researchers found that these tectonically produced cracks, which are about 100 million years old, must have been closed by the viscous flow of shale under stress.
Instead, Bažant and his colleagues hypothesized that the shale layer had weak layers of microcracks along the now-closed cracks, and it must have been these layers that caused branches to form off the main crack. Unlike previous studies, they also took into account the seepage forces during diffusion of water into porous shale.
When they developed a simulation of the process using this new idea of a weak layers, along with the calculation of all the seepage forces, they found the results matched those found in reality.
“We show, for the first time, that cracks can branch out laterally, which would not be possible if the shale were not porous,” Bažant said.
After establishing these basic principles, researchers hope to model this process on a larger scale.
This research was funded by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development program at Los Alamos National Laboratory, and the collaborating team at Los Alamos was funded by the U. S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. Other authors of the paper include Saeed Rahimi-Aghdam, Hyunjin Lee, Weixin Li, and Hoang Nguyen of Northwestern, and Viet-Tuan Chau, Satish Karra, Esteban Rougier, Hari Viswanathan, and Gowri Srinivasan of Los Alamos National Laboratory.